The Challenge of Calcification and Critical Limb Ischemia
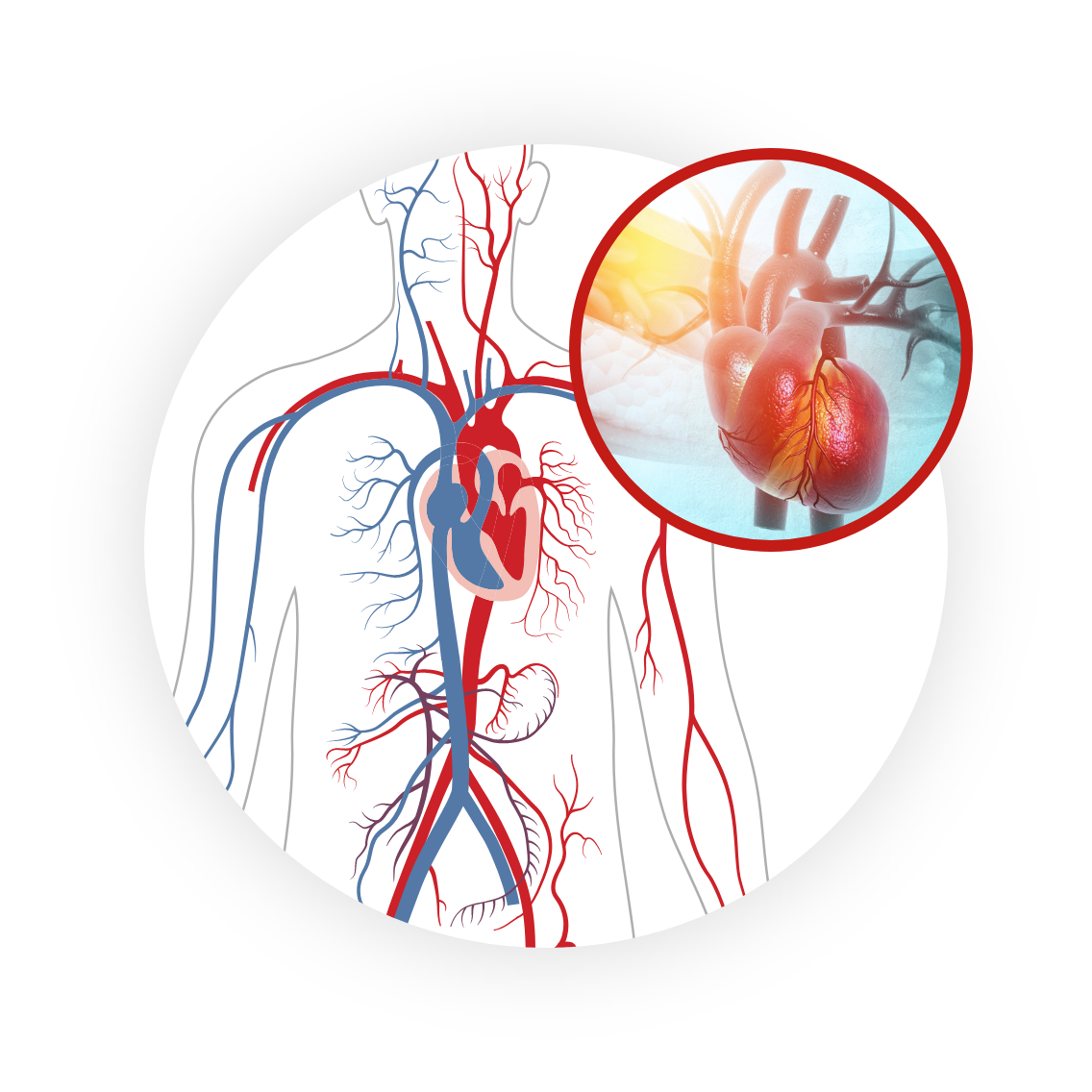
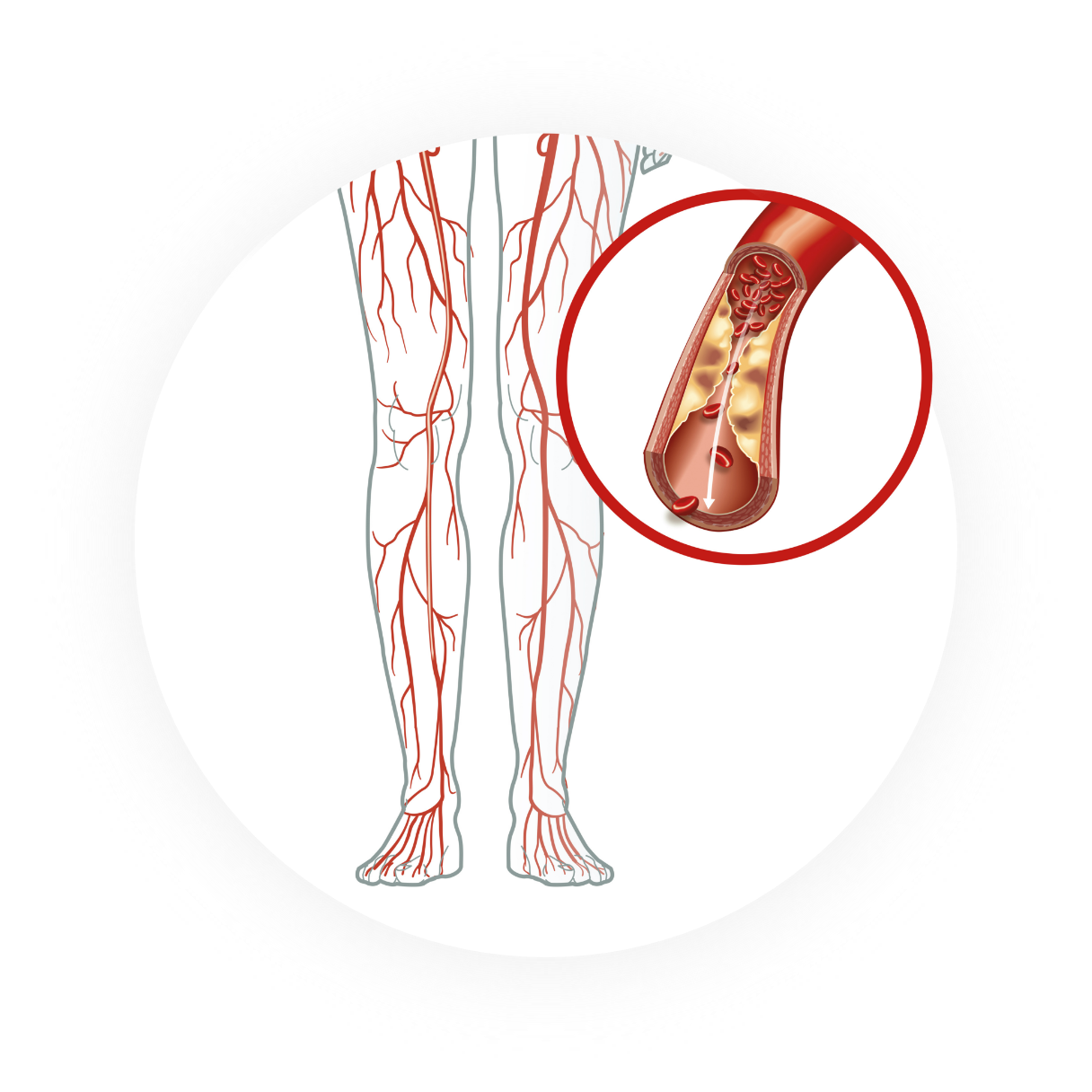
The cardiovascular community is primed for a novel and simple solution to enable physicians to address challenging and debilitating calcified vascular occlusions safely and effectively.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): A Worldwide Health Concern
PAD is a circulatory disease that results in the narrowing or blocking of arteries, reducing blood flow in the leg(s), which can lead to pain, swelling and even amputation1
- Global endemic affecting 200 million people worldwide, and 20 million people in the United States alone2
- ~ 25-30 million people worldwide and
>3 million in the United States alone are burdened with CLI2
Critical limb ischemia (CLI), the late-stage and worst form of PAD, has a poor prognosis. Within the first year of a CLI diagnosis…
- 25% of patients will die2,3,4
- 25% will have a major limb amputation as primary treatment, at a cost of $22 billion in the United States alone2,3,4
- Two years after below-the-knee (BTK) amputation, 15% will undergo above-the-knee (ATK) amputation and 30% will die4
Two years after below-the-knee (BTK) amputation, 15% will undergo above-the-knee (ATK) amputation and 30% will die4
- 50% of PAD and 65% of CLI patients have moderate or severe calcification
- Chronic total occlusions (CTOs) are encountered in up to 50% of PAD and CLI patients undergoing endovascular treatment
Despite technology development, current devices have limitations in cases with significant calcification5-7
- Failure rates remain high in revascularization procedures, with the biggest failure modality attributed to the inability to cross the tough fibrocalcific chronic total occlusion caps and lesion with a conventional guidewire
- There remains a significant unrealized demand for a novel technology solution to safely and effectively address highly calcific lesions and arrive at the interventional goal: restore flow, promote wound healing and prevent amputations
References:
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/peripheral-artery-disease
- Yost, Mary (The SAGE Group). The Cost of Critical Limb Ischemia, 2019.
- Abu Dabrh AM, et al. J Vasc Surg. 2015;62(6):1642–1651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgren L, et al. J Vasc Surg. 2007;45(suppl S):S5–S67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murabito JM, et al. Am Heart J. 2002;143(6):961–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanelli, J Cardiovasc Surg 2014.
- van der Heijden FH, et al. Br J Surg, 1993.